NR4A1 & Arylhydrocarbon Receptor Biology
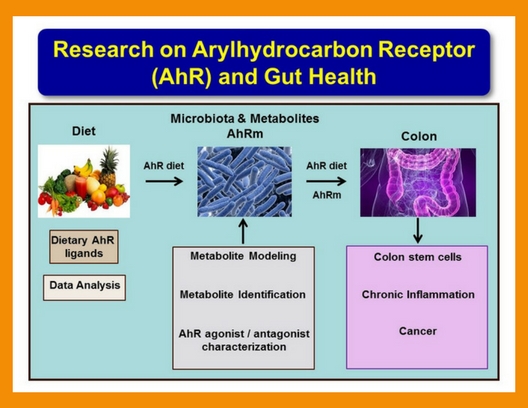
Investigation of the Role of Dietary and Microbial Ligands as Modifiers of Inflammation and Colon Cancer Development.
Projects in this research area are designed to assess how microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolites mediate AhR-dependent intestinal function. Since transformation of adult stem cells is an extremely important route towards initiating intestinal cancer, we have interrogated the effect of diet and microbiota-derived AhR ligands on intestinal stem cell homeostasis and colon tumorigenesis using tissue and stem cell-specific AhR knock out and control compound mice. This objective is supported by our novel preliminary data indicating that microbial-derived AhR ligands have a direct effect on the intestinal epithelium (without the contribution of the mesenchymal niche) and modulate stemness. In addition, we have demonstrated that microbiota-derived AhR ligand levels are decreased under high fat diet (obesogenic) conditions. This is noteworthy, because a growing body of preclinical and epidemiological data indicate that the risk of colon cancer is strongly associated with obesity.
Collectively, our results provide a critical new paradigm in understanding the molecular mechanisms through which microbes modulate colon cancer risk.
** View Dr. Chapkin’s interview with the American Institute on Cancer Research: Under the Microscope: AhR Microbes Holding the Keys to Your Gut Health?
- R.A. Debler, C.A. Madison, L. Hillbrick, P. Gallegos, S. Safe, R.S. Chapkin and S. Eitan. Selective aryl hydrocarbon receptor modulators can act as antidepressants in obese female mice. Journal of Affective Disorders 333:409-419, 2023. PMID: 37084978, PMCID: PMC10561895
- M. Lee, S. Upadhyay, F. Mariyam, A. Hailemariam, K. Lee, A. Jayaraman, R.S. Chapkin and S. Safe. Flavone and hydroxyflavones are ligands that bind the orphan nuclear receptor 4A1 (NR4A1). International Journal of Molecular Science 24:8152, 2023. PMID:37175855, PMCID: PMC10179475
- S. Safe, J. Kothari, A. Hailemariam, S. Upadhyay, L.A. Davidson andR.S. Chapkin. Health benefits of coffee consumption for cancer and other diseases and mechanisms of action. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24:2706, 2023. PMID: 36769029, PMCID: PMC9916720
- C.A. Madison, L. Hillbrick, J. Kuempel, G.L. Albrecht, K. K. Landrock, S. Safe, R.S. Chapkin, and S. Eitan Intestinal epithelium aryl hydrocarbon receptor is involved in stress sensitivity and maintaining depressive symptoms. Behavioural Brain Research, 319:213-220, 2022. PMID:36528169, PMCID: PMC9839636
- C.A. Madison, R.A. Debler, N.I. Vardeleon, L. Hillbrick, A. Jayaraman, S. Safe, R.S. Chapkin and S. Eitan. Sex-dependent differences in the stress mitigating and antidepressant effects of selective arylhydrocarbon receptor modulators. Journal of Affective Disorders 319:213-220, 2022. PMID: 36206882, PMCID: PMC10391660
- Hyejin Park, Un-Ho Jin, Gregory Martin, Robert S. Chapkin, Laurie A. Davidson, Kyongbum Lee, Arul Jayaraman, Stephen Safe. Structure-activity relationships among mono- and dihydroxy flavones as aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) agonists or antagonists in CACO2 cells. Science Direct. Available online 31 July 2022, Version of Record 4 August 2022. PubMed PMID:35917944, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2022.110067
- 3,3′-Diindolylmethane and 1,4-dihydroxy-2-naphthoic acid prevent chronic mild stress induced depressive-like behaviors in female mice. J Affect Disord. 2022 Jul 15;309:201-210. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2022.04.106. Epub 2022 Apr 21. PubMed PMID: 35461819; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC9153281.
- Yang, D. Osorio, L.A. Davidson, H. Han, D. Mullens, A. Jayaraman, S. Safe, I. Ivanov, J.J. Cai and R.S. Chapkin. Single cell RNA sequencing reveals how the aryl hydrocarbon receptor shapes cellular differentiation potency in the mouse colon. Cancer Prevention Research 15:17-28, 2022. PMID: 34815312, PMCID: PMC8741728
- R.S. Chapkin, L.A. Davidson, H. Park, U.H. Jin, Y.Y. Fan, Y. Cheng, M.E. Hensel, K.K. Landrock, C. Allred, R. Menon, C. Klemashevich, A. Jayaraman and S. Safe. Role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) in mediating the effects of coffee in the colon. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, 65(20):e2100539, 2021. PMID: 34406707, PMCID: PMC8530922
- Han, L.A. Davidson, K. Landrock, A. Jayaraman, S.H. Safe and R.S. Chapkin. Loss of arylhydrocarbon receptor suppresses the response of colonic epithelial cells to IL22 signaling by upregulating SOCS3. American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology 322:G93-G106, 2021. PMID: 34755534
- Han, S. Safe, A. Jayaraman, and R.S. Chapkin. Diet-host-microbiota interactions shape aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand production to modulate intestinal homeostasis. Annual Review of Nutrition 41:455-478, 2021. PMID:34633858, PMCID: PMC8667662
- Safe, A. Jayaraman, R.S. Chapkin, M. Howard, K. Mohankumar and R. Shretha. Flavonoids: Structure-function and mechanisms of action and opportunities for drug development. Toxicological Research 37:147-162, 2021. PMID:33868973, PMCID:PMC8007671
- Targeting the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in Stem Cells to Improve the Use of Food as Medicine. Current Stem Cell Reports 6:109-118, 2021. PMID: 34395177, PMCID:PMC8362759
- H. Han, L.A. Davidson, M. Hensel, J. Goldsby, G. Yoon, K. Landrock, C. Allred, A. Jayaraman, I. Ivanov, S.H. Safe and R.S. Chapkin. Loss of aryl hydrocarbon receptor promotes colon tumorigenesis in ApcS580/+; KrasG12D/+ mice. Molecular Cancer Research 19:771-783, 2021. PMID: 33495399, PMCID:PMC8137548
- Safe, U. Jin, H. Park, R.S. Chapkin and A. Jayaraman. Aryl hydrocarbon (AhR) ligands as selective AhR modulators (SAhRMs). International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21:6654, 2020, PMID: 32932962, PMCID:PMC7555580
- Safe, A. Jayaraman and R.S. Chapkin. Ah receptor ligands and their impacts on gut resilience: Structure-activity effects. Critical Reviews in Toxicology 50:463-473, 2020, PMID: 32597352, PMCID:PMC7773274
- H. Han, L.A. Davidson, Y.Y. Fan, J. Goldsby, G. Yoon, U. Jin, G.A. Wright, K. Landrock, B.R. Weeks, R.C. Wright, C.D. Allred, A. Jayaraman, I. Ivanov, J. Roper, S.H. Safe and R.S. Chapkin. Loss of aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling potentiates FoxM1 signaling to enhance self-renewal of colonic crypt Lgr5+ stem and progenitor cells. EMBO Journal 39: e104319, 2020. PMID:32915464, PMCID:PMC7527924
- K. He, S.M. Donovan, I. Ivanov, J. Goldsby, L.A. Davidson and R.S. Chapkin. Assessing the multivariate relationship between the human infant intestinal exfoliated cell transcriptome (exfoliome) and microbiome in response to diet. Microorganisms 8:2032, 2020. PMID:33353204, PMCID:PMC7766018
- F. Yang, J. DeLuca, R. Menon, E. Garcia-Villatoro, E. Callaway, K. Landrock, K. Lee, S. Safe, R.S. Chapkin, C. Allred and A. Jayaraman. Effect of diet and intestinal AhR expression on fecal microbiome and metabolomic profiles. Microbial Cell Factories 19:219, 2020. PMID:33256731, PMCID:PMC7708923
- Garcia-Villatoro, EL, DeLuca, JAA, Callaway, ES, Allred, KF, Davidson, LA, Hensel, ME et al.. Effects of high-fat diet and intestinal aryl hydrocarbon receptor deletion on colon carcinogenesis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2020;318 (3):G451-G463. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00268.2019. PubMed PMID:31905023
- Park, H, Jin, UH, Orr, AA, Echegaray, SP, Davidson, LA, Allred, CD et al.. Isoflavones as Ah Receptor Agonists in Colon-Derived Cell Lines: Structure-Activity Relationships. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2019;32 (11):2353-2364. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.9b00352. PubMed PMID:31621310 PubMed Central PMC6938648.
- Safe, S, Han, H, Goldsby, J, Mohankumar, K, Chapkin RS. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR) Ligands as Selective AhR Modulators: Genomic Studies. Curr Opin Toxicol. ;11-12 :10-20. doi: 10.1016/j.cotox.2018.11.005. PubMed PMID:31453421 PubMed Central PMC6709982.
- Jin, UH, Park, H, Li, X, Davidson, LA, Allred, C, Patil, B et al.. Structure-Dependent Modulation of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor-Mediated Activities by Flavonoids. Toxicol. Sci. 2018;164 (1):205-217. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfy075. PubMed PMID:29584932 PubMed Central PMC6016704.
- Jin UH, Cheng Y, Park H, Davidson LA, Callaway ES, Chapkin RS, Jayaraman A, Asante A, Allred C, Weaver EA, Safe S. Short Chain Fatty Acids Enhance Aryl Hydrocarbon (Ah) Responsiveness in Mouse Colonocytes and Caco-2 Human Colon Cancer Cells. Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 31;7(1):10163. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-10824-x. PMID:28860561
- Cheng Y, Jin UH, Davidson LA, Chapkin RS, Jayaraman A, Tamamis P, Orr A, Allred C, Denison MS, Soshilov A, Weaver E, Safe S. Editor’s Highlight: Microbial-Derived 1,4-Dihydroxy-2-naphthoic Acid and Related Compounds as Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Agonists/Antagonists: Structure-Activity Relationships and Receptor Modeling. Toxicol Sci. 2017 Feb;155(2):458-473. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfw230. Epub 2016 Nov 11. PMID:27837168
- Ying W, Tseng A, Chang RC, Morin A, Brehm T, Triff K, Nair V, Zhuang G, Song H, Kanameni S, Wang H, Golding MC, Bazer FW, Chapkin RS, Safe S, Zhou B. MicroRNA-223 is a crucial mediator of PPARγ-regulated alternative macrophage activation. J Clin Invest. 2015 Nov 2;125(11):4149-59. doi: 10.1172/JCI81656. Epub 2015 Oct 5. PMID:26436647
- Fan YY, Davidson LA, Callaway ES, Wright GA, Safe S, Chapkin RS. A bioassay to measure energy metabolism in mouse colonic crypts, organoids, and sorted stem cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2015 Jul 1;309(1):G1-9. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00052.2015. Epub 2015 May 14. PMID:25977509
- Cheng Y, Jin UH, Allred CD, Jayaraman A, Chapkin RS, Safe S. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Activity of Tryptophan Metabolites in Young Adult Mouse Colonocytes. Drug Metab Dispos. 2015 Oct;43(10):1536-43. doi: 10.1124/dmd.115.063677. Epub 2015 Apr 14. PMID:25873348
- Jin UH, Lee SO, Sridharan G, Lee K, Davidson LA, Jayaraman A, Chapkin RS, Alaniz R, Safe S. Microbiome-derived tryptophan metabolites and their aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent agonist and antagonist activities. Mol Pharmacol. 2014 May;85(5):777-88. doi: 10.1124/mol.113.091165. Epub 2014 Feb 21. PMID:24563545
